Time Dilation Explained in Detail
Introduction: What is Time Dilation ?
Einstein's special theory of relativity had three important
consequences for very fast moving objects. First, the time for the people
sitting inside a fast moving object will pass slower than those who are looking
at the object from outside. That is, if you stand on earth and see a vehicle
whose speed is around the speed of light, then the time for people sitting
inside it will pass slower than you. This is what we call Time Dilation.
Second, if an object is moving at a speed close to the speed of light, then the
observer standing outside will see that object smaller than its original size.
That is, for the observer standing outside, the length of that object will
appear contracted. This is what we call Length Contraction. Third, when the
speed of an object is near the speed of light, its mass increases much more
than its original mass. That is, as the speed of an object increases, its mass
also increases.
In this post I am going to explain you about what is time
dilation and why does time dilation occur. But to understand time dilation, some basic things have to
be understood first. For example, there are no such things like absolute rest
and absolute motion.
Absolute Rest and Absolute Motion
There
are no such things as absolute rest and absolute motion. That is, nothing is
ever in the state of complete rest or complete motion. It is always relative to
someone. To understand this suppose you are sleeping. When you wake up from
sleep, you find that you are in a room whose windows and doors are closed.
Until you open those windows, you feel that you are in a room that is stable.
But as soon as you open the windows, you find that everything outside the room
is seen going backwards from you, which shows that you are inside a van which
is constantly moving. That is, as long as you were inside the room of that van,
you felt that the room was stopped. While a man standing outside was seen
moving the same van. This shows that rest and motion are relative rather than
absolute. Now you will think that my house always stays in one place. So that
is an absolute rest. But you also know that you are wrong. Your house is in
rest only in your respect while our earth is rotating continuously and your
house is also moving along with the earth. That is, your house is in motion in
respect to the man standing in space while in your respect your house is in
rest. That is why rest and motion are relative instead of absolute. I hope you have understood that without any reference frame we cannot decide what is in rest and what’s in motion.
Assumptions of Einstein’s Special Theory of Relativity
Einstein
used two assumptions in his special theory of relativity. First, the laws of
physics apply uniformly to every corner of the universe and second, the speed
of light is always constant for all observers in a fixed medium. That is,
whether you are standing fixed or sitting in a car moving at a high speed,
whenever you measure the speed of light, it will always come to 300,000 km / s.
As we know that if the reference frame changes in normal life then the relative
velocity also changes accordingly. But this does not happen with the speed of
light. That is, whatever the reference frame is, the speed of light never
changes. This is little difficult to digest. But this is true because it has
been confirmed by many experiments.
What is Time Dilation in Detail ?
Suppose
you have a simple light clock with mirrors on both the top and bottom. A sensor
is also attached to the bottom mirror which records the reading when the light
reflects from the top mirror and hits the bottom mirror. Suppose for a moment
that the distance between the top and bottom mirrors is x. Now light will take
some time to cover this distance. Let's consider that time as t. Since we know
that the speed of light is c (c = 300,000 km / s). We can say that x = ct
(distance = speed × time). Now suppose that we put this light clock in a
vehicle whose speed is around the speed of light. Everyone sitting in that
vehicle will feel light clock normal. They will feel that the light is moving
up and down in that light clock in a very straight way. But Observer, standing
outside the vehicle, will get a different view. Since this vehicle is in
motion, the light clock is also in motion. Now the diagonal path has to be
replaced by the straight path for the light to go from top to bottom.
Obviously, the distance of the diagonal path is more than the straight path.
That is, in this case light has to travel more distance. We know that speed =
distance / time and we also know that the speed of light is always remains same
in a fixed medium whether the observer is stationary or moving. Since the
distance covered by the light has increased compared to earlier, the time also
has to be increased to keep the speed of light same. Let us understand this
with an example. We know that the speed of light is about 300,000 kilometres per
second, but to make the example easy, we just consider it 3 meters per second.
Now suppose that the distance between the two mirrors of the light clock is 6
meters. That is, the light has to travel 6 meters to reach from one mirror to
another. From the formula of speed = distance / time, light will take 2 seconds
to cover this distance. Talking about the second case, the light is moving
diagonally for the Observer standing outside the vehicle. In such a situation,
the distance traveled by light will be more than 6 meters. Suppose it is 9
meters. Now the speed of light is constant at 3 meters per second. Now if we find
the time again with speed = distance / time formula, then it will come 3 seconds.
That is, 3 seconds would have passed for the Observer standing outside the
vehicle, while for the people sitting inside the vehicle, only 2 seconds would
have passed. This dilation of time is called time dilation. This was a simple
example to explain time dilation. You can also find the exact magnitude of time
dilation by a formula given below-
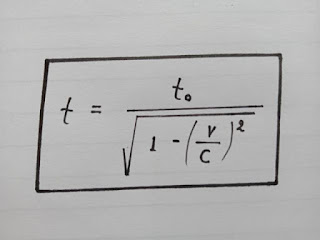 |
| Time Dilation Equation |
where,
t = time for the people inside the vehicle or time in motion or dilated time
t = time for the people inside the vehicle or time in motion or dilated time
t (not)= time for people outside the vehicle or time
at rest or stationary time
v = velocity of vehicle or
simply velocity
c = speed of light
c = speed of light
This example was bit difficult to explain. But still I hope you guys understood what is time dilation. Please share this post as much as possible.
Thank U


Please do not enter any spam link in the comment box. ConversionConversion EmoticonEmoticon